Ecospray has been studying a range of different solutions to decarbonize the maritime sector over recent years, and is now ready to introduce the carbon reduction journey to the market.

R&D is in Ecospray’s DNA. EGCS and bio-LNG plants are good examples of products that were developed from a concept: going through engineering, they have been extensively tested and successfully installed on board ships and in land-based applications. We are now working on different R&D projects that will contribute to the big challenge facing both shipping and land-based industries: reducing CO₂ emissions in the short term and helping shipping become a zero CO₂ emissions industry in the long run.
Ecospray is capitalizing on the experience and know-how it has gained from exhaust gas cleaning to support shipowners on the path towards decarbonization: we are using our expertise to help the industries we work with in making this possible.
Ecospray has mapped out a path towards decarbonization that extends beyond the Marine sector. Our journey towards clean energy creation has led us to reach significant milestones: these include using carbon-neutral fuels, such as bio-LNG – which we have been working on since 2018. In the last few months, construction has started on different plants, which include CO₂ capture and liquefaction, and we are increasing our commitment in this sector with new contracts.
In recent years, Ecospray has also been studying a range of different solutions to support decarbonization: in fact, the development of various carbon-capture technologies is one of the projects that we are investing the most in, for both land transport and the marine sector, and we will soon be ready to introduce them to the market.

We started thinking about how to support our customers in the decarbonization challenge. We have a history of developing solutions that are based on customers’ needs and investing in R&D. Focusing on carbon dioxide removal was a natural evolution, given our expertise in removing pollutants from exhaust gas.
We studied three Carbon Capture technologies in collaboration with universities and research centers – fuel cells with the Department of Civil, Chemical and Environmental Engineering at the University of Genoa, and carbon capture using amines and calcium hydroxide with the Department of Earth Sciences at the University of Turin. The technologies are each at different stages of development, and their suitability varies depending on the application, ship size, operating profile, type of vessel etc.

Carbon capture with amines
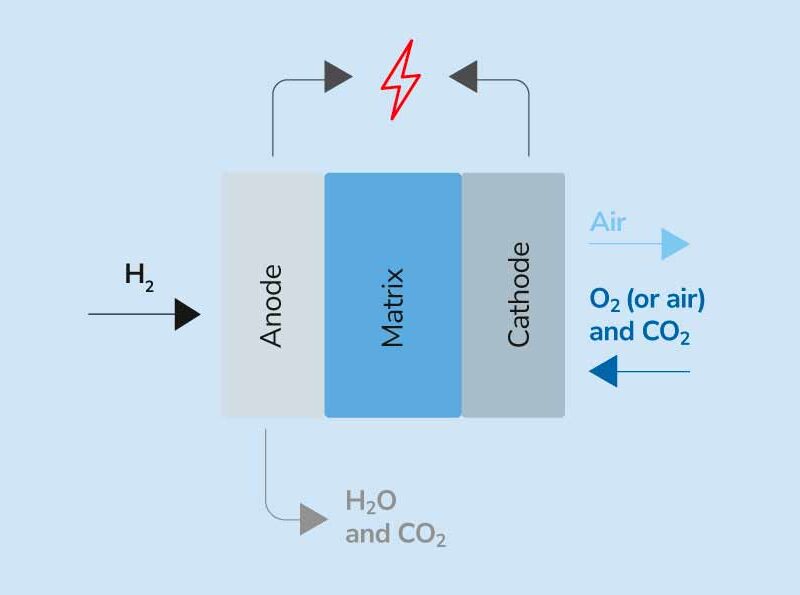
Ecospray is developing amine absorption technology for CCS in onboard marine applications, based on an approach that is well-known in the CO2 production industry. Our amine-based chemical absorption technology will be the first to be implemented with the main goal of reducing the dimensions and complexity of the system. Another key focus is process optimization for power consumption, using the thermal energy available on board.
This technology is reliable and safe, thanks to the non-hazardous nature of the chemical used.
CO2 is absorbed by the amine solution, which is then regenerated during the process by stripping the CO2 out of it. Once separated, the CO2 is liquefied and stored in specific cryogenic tanks on board.
Carbon capture with calcium hydroxide
Another approach Ecospray is studying is CO2 adsorption with lime milk, a suspension of calcium hydroxide in water with a solid content ranging from 10% to 30%. Calcium oxide reacts with CO2 to form calcium carbonate, which is only slightly soluble in water, so it forms a solid product.
This technology is particularly interesting in terms of Capex and Opex. Bulk carrier ships are the main target for this solution, which requires bulk onboard storage of the chemical reagent, but it has the advantage of not requiring onboard CO2 storage.
Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFC)
The third solution involves a new generation of Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells, it combines high-efficiency clean power generation and carbon capture in the same equipment. This technology is undoubtedly the most complex, but can ensure very low Opex along with greater carbon reduction capabilities, both as a result of fuel savings.
This technology can be also integrated with other Ecospray environmental solutions such as DeSOx, particle filters, and oxidation catalysts. Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells can be powered by methane (LNG, bio-LNG), hydrogen, ammonia, syngas and other fuels, reforming/cracking externally or directly inside the cell.

As a matter of fact, we are working on a pilot project for the two-chemical absorption-based technologies, which are already in the test phase in our laboratories. Our goal is to begin testing in real conditions on a cargo vessel in Q4 this year, with the subsequent scale-up starting in early 2023. Meanwhile, for the fuel cell-based solution, we are planning to have the first real-scale prototype of our Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFC) ready by the end of 2022, with onboard testing during 2023. Ideally, the first onboard installation will be on an LNG-fueled vessel.
Alberto Di Cecio, General Manager, is satisfied to say that
Our technology portfolio has significantly increased over the last three years, with “decarbonization” and “GHG emissions reduction” being the main drivers.
We took a holistic approach to dealing with these two drivers, trying to address the complex and impactful topics from several different angles.
Now, thanks to significant investment and relevant partnerships in R&D projects, we can offer the following technologies:
- WESP (Wet ElectroStatic Precipitator): capable of removing humidity, condensable species and up to 99% PM from exhaust gases downstream of a DeSOx EGCS, this technology is a real “carbon capture enabler”, ensuring extremely low levels of pollutants and removing visible emissions at the stack;
- DeNOx: our new range of catalysts enables high performance, compact design and robustness at the same time;
- Methane Slip Abatement: removing up to 90% of the methane slip from LNG-fueled engines will be possible from Q1-2023 thanks to our new catalytic solution, with significant beneficial effects on GHG emissions (and most likely on the CII (Carbon Intensity Indicator);
- Bio-LNG: our complete microscale systems for biogas upgrading and liquefaction have proved to be a successful product since Q3-2021, with increasing interest from customers in 2022. We are currently working on 3 projects for the German market (combined production of 15 ton/d, all fitted with the optional CO2 separation and liquefaction system) and 3 projects for the Italian market (combined production of 21 ton/d). Our next goals are to consolidate our position in the European market, and to approach the American market by the end of 2022.